
 Parallelogram Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. I Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Elliptical And Semi Elliptical Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Diamond Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Circular Pipe Cross Section Calculators. Circular And Semi Circular Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Beam Section Modulus Calculation Module. Beam Cross Section Parallel Axis Theorem Calculation Module. Beam Cross Section Concrete Stiffness Factor Calculation Module.
Parallelogram Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. I Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Elliptical And Semi Elliptical Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Diamond Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Circular Pipe Cross Section Calculators. Circular And Semi Circular Beam Cross Section Calculation Module. Beam Section Modulus Calculation Module. Beam Cross Section Parallel Axis Theorem Calculation Module. Beam Cross Section Concrete Stiffness Factor Calculation Module. 
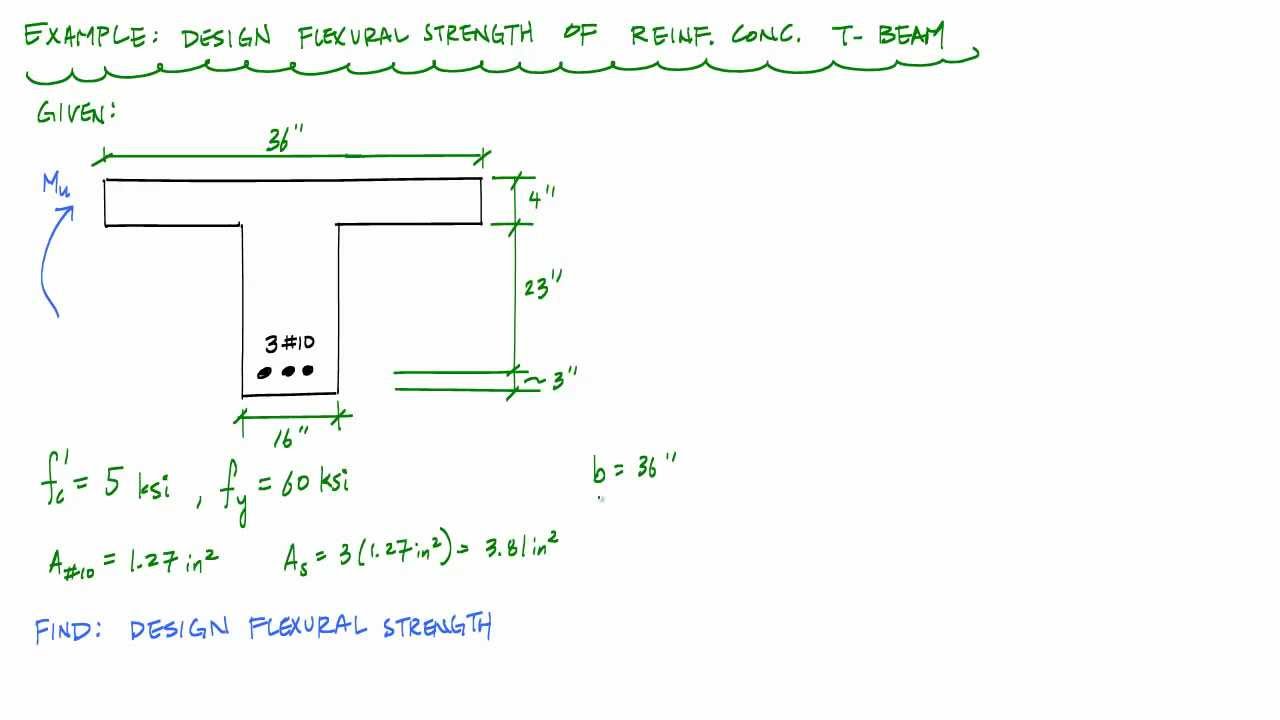
Beam Cross Section Added Mass Calculation Module.Reference : Roark's Formulas For Stress And Strain, Warren C Young, McGraw Hill Change Module : The Tee section is assumed to be symmetrical along axis 2, and the flanges are assumed to be equal length and thickness. An axis is fixed and then the second moment of area of each shape is calculated and summed to the area multiplied by the distance between the fixed axis and the shape centroid squared.Calculate beam cross section properties for T section beams: cross section area, moment of inertia, polar moment of inertia, mass moment of inertia, section modulus, radius of gyration, EI, EA, EAα, unit mass, total mass, unit weight and specific gravity. The parallel axis thereom is used to seperate the shape into a number of simpler shapes. If the shape is more complex then the moment of inertia can be calculated using the parallel axis thereom.The moment of inertia can be calculated by hand for the most common shapes: How is the moment of intertia or second moment of area calculated?
The second moment of area (otherwise known as moment of inertia) is a a measure of a shapes resistance to angular acceleration.The moment of inertia (otherwise known as second moment of area) is a a measure of a shapes resistance to angular acceleration.This can either be the elastic section modulus which considers the strength of the beam up to elastic yielding or the plastic section modulus which considers strength up to plastic yielding. The section modulus (otherwise known as the first moment of area) is a parameter which measures a section strength in bending.Where I is the second moment of area of a shape and A is the area.

The radius of gyration is calculated using the formula. How is the radius of gyration calculated? The radius of gyration of a shape is the distance between the shapes axis of rotation and the shapes centre of gravity. There is no difference between the centroid of a shape and the centre of gravity, the terms can be used interchangeably. What’s the difference between the centroid of a shape and the centre of gravity? This summed value is then divided by the total area of all combined component shapes to give the centroid. To find the centroid, the individual centroids of each component shape are determined, the idividual centroid are then multiplied by the area of the correponding shape and summed. The centroid of a complex shape can be calculated using hand calculation methods, by using the Method of Geometric Decomposition. How is the centroid of a shape calculated? The centroid of a shape (otherwise known as the centre of gravity) is the geometric centre of the object and if the shape possesses an axis of symmetry this is where the axis will be located. There is no difference between the second moment of area and the moment of intertia, the terms can be used interchangeably. What’s the difference between moment of inertia and second moment of area? The moment of inertia (otherwise known as the second moment of area), is a measure of the 'efficiency' of a cross-section to resist bending, caused by applied forces. The second moment of area (otherwise known as the moment of inertia), is a measure of the 'efficiency' of a cross-section to resist bending, caused by applied forces.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
